

Let’s learn the salary formula with the following examples by creating a salary sheet in excel with formula. Income Tax, Professional Tax, TDS, EPF, ESIC, etc.ĭepending on the Income Tax Act of 1961 provisions, some allowances may be fully or partially exempt from tax, while others may be taxable.Įxamples of Salary Formula (With Excel Template)
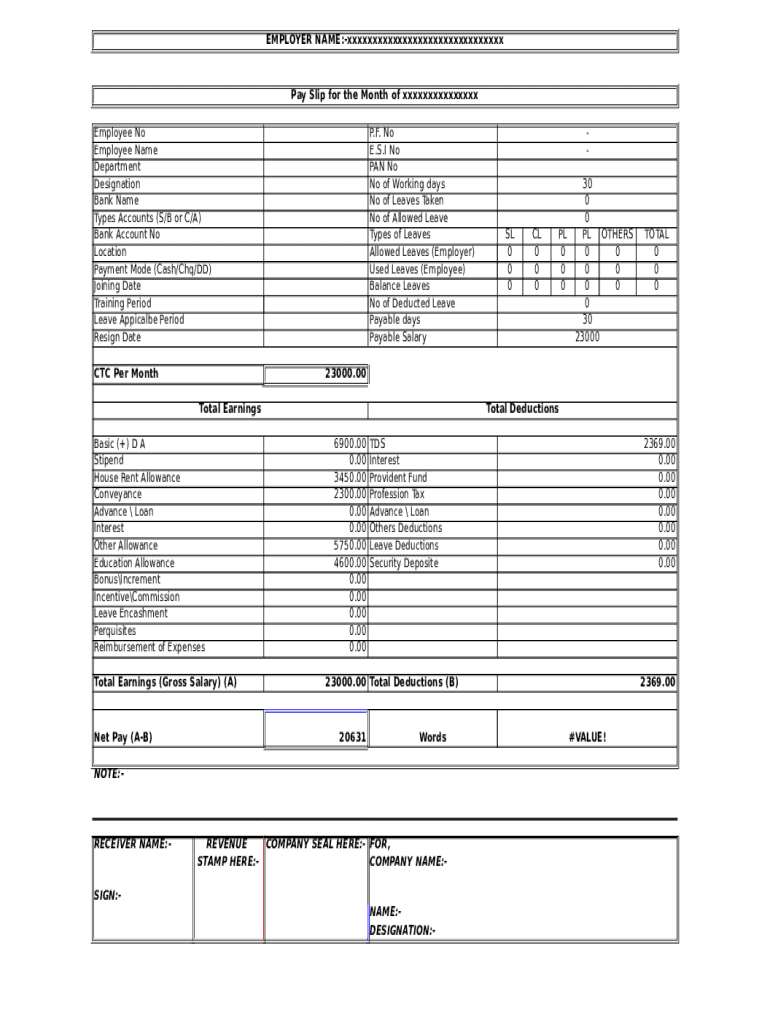
Perquisites (e.g., car for personal use, rent-free accommodation, phone, internet services, etc.) Net salary = Gross Salary – Income Tax – Professional Tax – TDS – EPF – ESICĪllowances (DA, HRA, LTA, Conveyance, Medical, Special, etc.) Gross salary = Basic Salary + HRA + Other Allowances The amount of salary that is credited to your bank account after all deductions.īasic Salary = Gross Salary – Total Allowances (DA + HRA + Medical Insurance + Other Allowances) The amount of salary after adding all benefits and allowances to basic pay but before deducting any taxes. The fixed amount of salary before any addition of allowances and deductions of taxes. The table below provides an overview of the differences: Salary Component Net Salaryīefore we delve into using the salary formula to calculate various types of salaries, we must understand the distinctions between salary computation format. In the United States, salaries are often defined by pay scales or hourly wages. On the other hand, employees in the informal sector typically receive their full salary amount. In India, for instance, companies often operate under a cost-to-company (CTC) model, which means that formal sector employees experience several deductions from their salary.

Some companies might include additional deductions not mentioned above, while others may have fewer deductions. Additionally, individual companies may have their policies regarding salary components.
The salary structure can vary significantly between countries due to cultural norms, economic factors, industry practices, job market conditions, cost of living, and local labor laws. Salary = Basic + HRA + Transport Allowance + FBP Allowance + Bonus – Provident Fund – Income Tax – Insurance


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
